Access Token Manipulation
27 October 2023 / Written by Pedro Lima (boloto1979)
TL;DR Is a cybersecurity technique with both legitimate and malicious applications. This method involves obtaining, modifying, or misusing access tokens used in authentication and authorization systems.
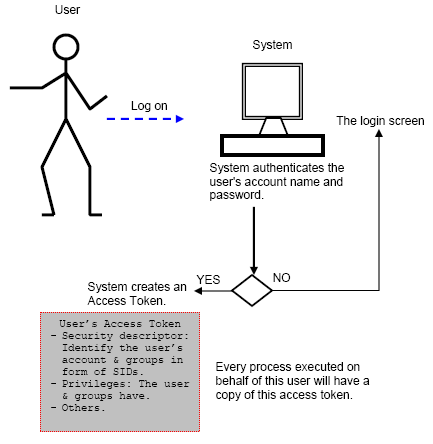
“Access Token Manipulation” refers to a cybersecurity technique used to obtain, modify, or abuse access tokens in authentication and authorization systems. Access tokens are used in authentication systems to confirm a user’s identity and grant permissions to access resources or perform specific actions.
This technique can be used legitimately by applications and services to access resources on behalf of an authenticated user. However, in cybersecurity contexts, access token manipulation usually refers to malicious activities where an attacker attempts to exploit vulnerabilities in a system to obtain, modify, or misuse third-party access tokens.
Some common forms of Access Token Manipulation include:
-
Token Theft: An attacker may try to steal access tokens from a legitimate user, such as intercepting them during transmission or exploiting security vulnerabilities.
-
Token Reuse: The attacker may attempt to reuse a valid access token after obtaining it, taking advantage of its validity to access resources or perform actions on behalf of the legitimate user.
-
Token Modification: This involves altering a valid access token to grant additional permissions or modify parameters to carry out malicious actions.
-
Privilege Escalation: An attacker may attempt to elevate their own privileges by manipulating access tokens to gain access to resources or functionalities they would not normally have permission for.
It’s important to note that access token manipulation is a significant security threat to systems and applications that rely on authentication and authorization. To mitigate these threats, it’s necessary to implement robust cybersecurity practices, such as properly securing tokens, monitoring suspicious activities, and adopting security measures like multi-factor authentication and encryption whenever possible.
Legitimate Use Cases
While access token manipulation is often associated with malicious activities, there are legitimate use cases where applications use this technique. For example, in federated authentication systems, a service may manipulate an access token to access resources from another service on behalf of an authenticated user, as seen in Single Sign-On (SSO) with third-party services or social networks.
OAuth 2.0 and Access Tokens
The OAuth 2.0 protocol is widely used to grant access to resources in third-party systems. It utilizes access tokens, often called “Bearer Tokens,” to authorize requests. The security of access tokens is crucial for system integrity, and authentication providers should implement security measures, like token expiration, to reduce the risk of manipulation.
Token Theft and Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
In token theft scenarios, attackers may use techniques like Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks to intercept access tokens during communication between a client, an authorization server, and a resource server. This can occur in unsecured public networks or in untrustworthy mobile applications. To mitigate this, communications should be protected through encryption, and multi-factor authentication can be used to make token theft more challenging.
Data Security Implications
Access token manipulation can have serious data security implications. If an access token is stolen and misused, a user’s sensitive data can be compromised. Therefore, organizations must implement robust security practices, such as monitoring authentication events, logging suspicious activity, and token revocation policies.
Privilege Elevation and Authorization Policies
Access token manipulation can also be used for privilege escalation, allowing an attacker to access resources or perform actions that would normally be prohibited. To mitigate this risk, systems should implement strict authorization policies that check whether a user has the appropriate permissions before granting access to resources.
In conclusion, Access Token Manipulation is a technique that can be used both legitimately and maliciously in authentication and authorization systems. Security is paramount to protect access tokens and ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive resources and data. Implementing best security practices is essential to prevent and detect malicious activities related to token manipulation.
This repository contains two versions of the ATM (Assume The Identity of Another User) tool:
- ATM.cpp - Windows version
- unix_ATM.cpp - Linux version
Both versions aim to assume the identity of another user on the operating system where they are being executed, allowing a process to run with the privileges of that specific user.
ATM.cpp - Windows Version
Features:
- Assumes the identity of another user on the Windows system to execute a process with that user’s privileges.
- Uses Windows API functions related to security and token management to gain access to a specific process and create a new process on behalf of the desired user.
- Allows specifying the PID (Process ID) of the process from which you want to assume the identity.
Usage:
- Compile the program using a C++ compiler that supports Windows libraries.
- Run the program as an administrator or with elevated privileges to allow access to the required tokens and privileges.
- Fill in the value of the
pid_to_impersonatevariable with the PID of the process you want to assume the identity of. - The program will request access to the token of the specified process, enable the SE_DEBUG_NAME privilege for debugging purposes, and then create a new process with the duplicated token on behalf of the desired user.
Note: Be cautious when using this program, as assuming the identity of other users without proper authorization may be a security violation.
unix_ATM.cpp - Linux Version
Features:
- Executes a process on the Linux system with superuser privileges (root) from the beginning.
- Allows specifying the PID of the process you want to assume the identity of.
- Creates a new process on behalf of the desired user.
Usage:
- Compile the program using a C++ compiler compatible with the Linux system.
- Run the program with superuser privileges (root) to enable it to create processes with the necessary privileges.
- Fill in the value of the
pid_to_impersonatevariable with the PID of the process whose identity you want to assume. - The program will create a new process with superuser privileges and the identity of the user associated with the specified PID.
Note: Running programs with superuser privileges can be dangerous and should be done with extreme caution, only for legitimate and authorized purposes.
Security Warning:
Both versions of the tool are intended for educational purposes and should not be used for malicious purposes or without proper authorization. Manipulating user identities and privileges is a critical security issue and should be done responsibly and only on systems where you have permission to perform such actions. Misusing these tools may lead to legal consequences and significant harm.
Use these tools with care and responsibility.